Product Configuration and Feature Overview
Package Contents
Use the instrument in the following configuration.
MicroPeckerX CAN FD Analyzer


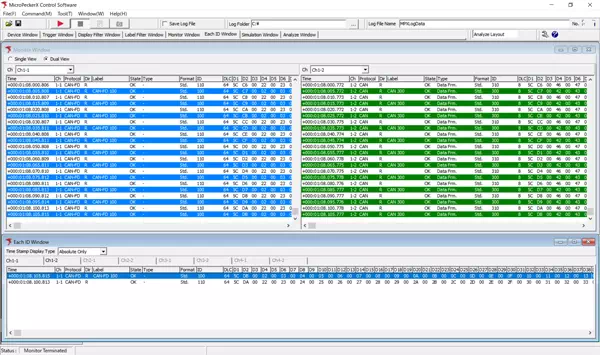
MicroPeckerX Control Software (GUI application)
Download from the Sunny Giken website.
CAN Cables
Combine CAN cables according to your use case.
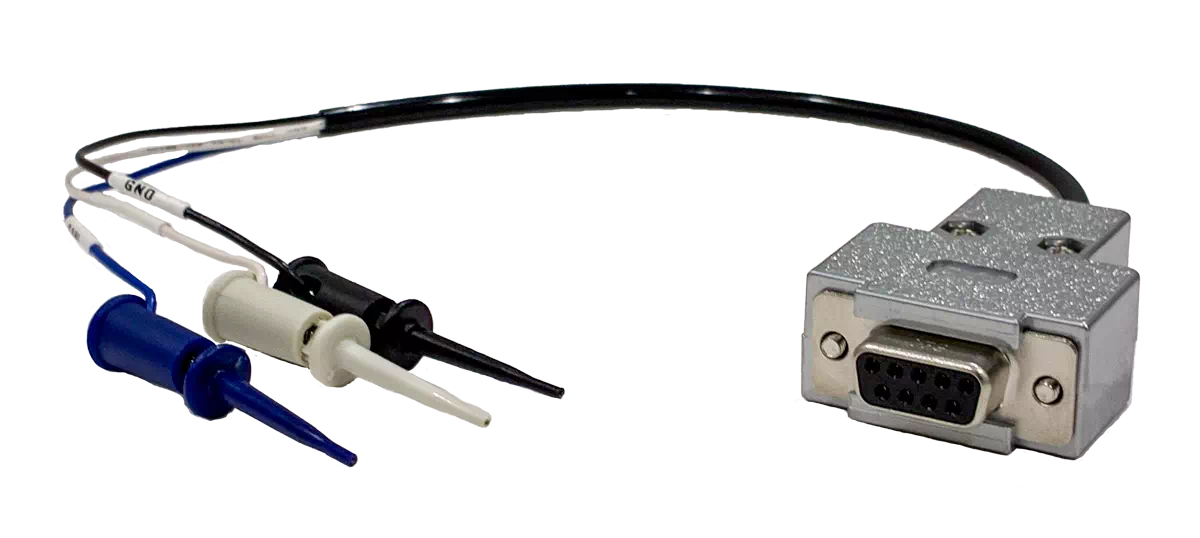
Model: S810-MX-CB1
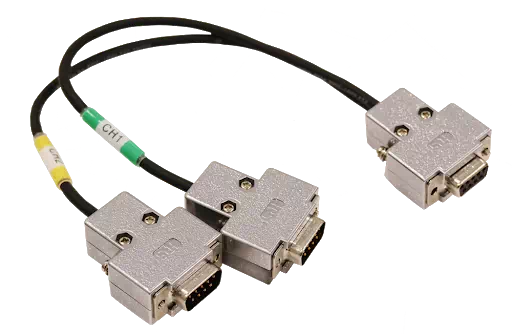
Model: S810-MX-CB2
Feature Overview
The analyzer offers the following major functions.
MicroPeckerX CAN FD Analyzer
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Monitoring | Streams CAN bus frame data in real time. • Start/stop logging with trigger detection • Frame filtering • Labeling and highlighting arbitrary frames • Dedicated views for a fixed ID |
| Simulation | Supports multiple transmission modes. 1. Slot transmission • Register up to 28 frames and send ad-hoc frames instantly • Periodic / event / event-periodic / direct transmission 2. Log replay mode 3. Burst transfer mode |
| Analyze | Assists with loading and investigating log data. �• Automatic/manual log import • Data search • Filter views • Channel log merge • Frame interval measurement • Gateway delay measurement • Gateway frame loss measurement • Gateway dwell time measurement |
System Configuration Diagram
Example System
The diagram below shows a typical configuration.
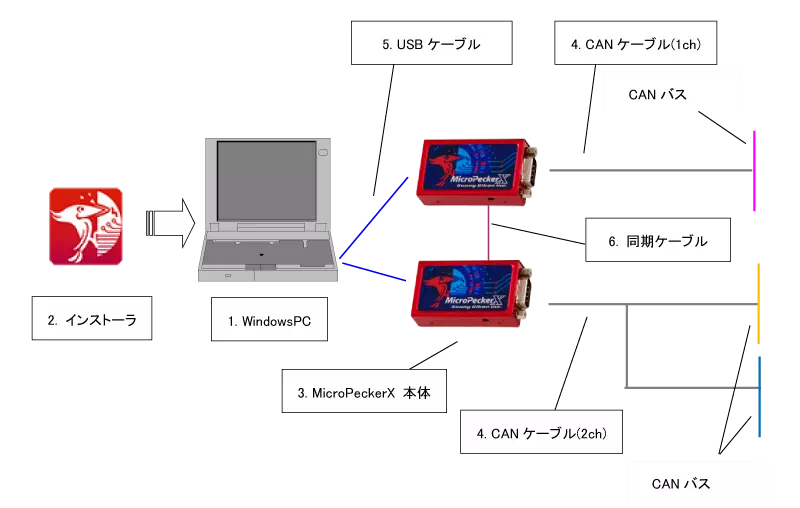
| No. | Device | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Windows PC | Runs the GUI application for setting up conditions and reviewing CAN monitor data. |
| 2 | Installer | Required when installing or upgrading the software package (GUI application, USB driver). |
| 3 | MicroPeckerX main unit | Connect to the PC via the USB cable and to the CAN bus via the CAN cable. When using multiple units, daisy-chain them with the sync cable. |
| 4 | CAN cable | Connects the MicroPeckerX to the CAN bus. Use the 1ch cable (CB1) or 2ch cable (CB2) as appropriate. |
| 5 | USB cable | USB 2.0 Micro-B cable for connecting to the PC. |
| 6 | Sync cable | Sync cable for operating multiple MicroPeckerX units in sync. |
Operating Environment
Use the control software on a PC that meets the following requirements.
| Item | Specification |
|---|---|
| OS | Windows 11 (64-bit), Windows 10 (64-bit), Windows 8.1 (64-bit) [*1] [*2] |
| CPU | Intel or AMD x86 processor (Core i5 / Ryzen 5 or higher recommended) |
| Disk space | At least 10 GB free [*3] |
| Memory | 8 GB or more recommended |
| USB ports | USB 2.0 (Hi-Speed) ports. Prepare one port per MicroPeckerX in use [*4] |
| Display | 1920 × 1080 or higher recommended |
| Other | Monitor, keyboard, and mouse |
[*1] Disable PC power-saving features such as sleep, disk stop, or CPU throttling while using the analyzer.
[*2] Virtualized environments are not supported.
[*3] Secure sufficient disk space if you plan to log for extended periods.
[*4] When using an external USB hub, choose a self-powered model and supply power externally. Bus-powered hubs can cause instability or malfunction.
Terminology
The following glossary explains the terms used in this guide.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| CAN | Controller Area Network. An automotive communication protocol standardized in ISO 11898. |
| CAN FD | CAN with Flexible Data-rate. An extension of CAN that enables faster and larger data transfers. Standardized as ISO 11898-1:2015. |
| MicroPeckerX | Collective name for the hardware platform equipped with automotive communication interfaces. Used together with applications for data acquisition and analysis. |
| Arbitration | Identifier (ID) field at the start of a CAN frame. Determines priority when multiple nodes request transmission simultaneously and controls bus access. |
| Payload | Data field of a CAN frame. Stores the raw signal values: up to 8 bytes (CAN) or 64 bytes (CAN FD). |
| Ch | Abbreviation for channel. Represents a physical or logical CAN communication path. MicroPeckerX supports multiple channels (for example Ch1-1, Ch1-2) that can operate independently. |
| GW | Gateway. Hardware or software that relays data between networks using different communication protocols. |
| Monitoring | Displays CAN bus data on the GUI application in real time. |
| Logging | Automatically saves CAN bus data to PC folders as text files (.csv). |
| Physical value | Actual engineering value calculated as signal value × resolution + offset or (signal value + offset) × resolution. |
| Signal value | Raw data stored in the payload of CAN/CAN FD frames before conversion. |
| Log replay | Reproduces previously captured log files. |
| Burst transfer | Sends frames or logs continuously to place high load on the CAN bus. |