Workflow for Using the Analyzer
This chapter explains the full workflow, from connecting the MicroPeckerX CAN FD Analyzer to reviewing and analyzing the captured logs.
1. Connect the Hardware
Connect MicroPeckerX using the bundled USB cable to a USB port on the Windows PC, then connect MicroPeckerX to the CAN bus.

- Incorrect wiring may damage both MicroPeckerX and the target system.
- If you use MicroPeckerX through a USB hub, bus power from the PC alone may be insufficient. Use a self-powered USB hub that has an external power supply.
2. Launch the GUI
Launch the GUI application with the following steps.
- Open the Windows Start menu.
- Expand All apps → MicroPeckerX.
- Select MicroPeckerX Control Software → MicroPeckerX Control Software Ver.X.XX (X.XX indicates the installed version).
Toolbar
You can freely arrange the toolbar and each window. Adjust the layout to suit the size of your monitor.
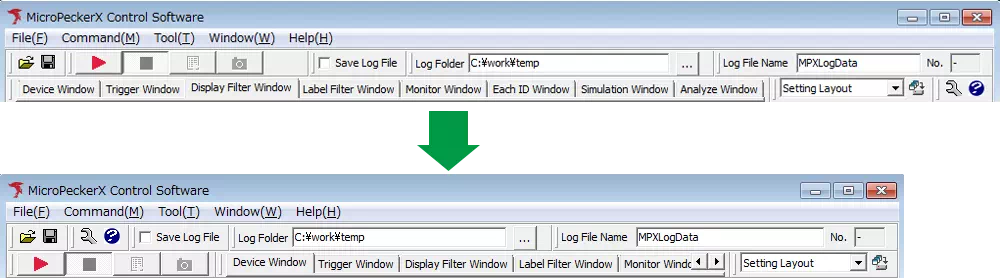
Save and Recall Layouts
Save window layouts with a custom name so you can recall them at any time.
- You can edit or delete layout names whenever needed.
- Register frequently used layouts in advance to improve your workflow.
- Save the current layout
From the toolbar menu, follow the steps below to save the layout.
Window → Layout → Save Current Layout
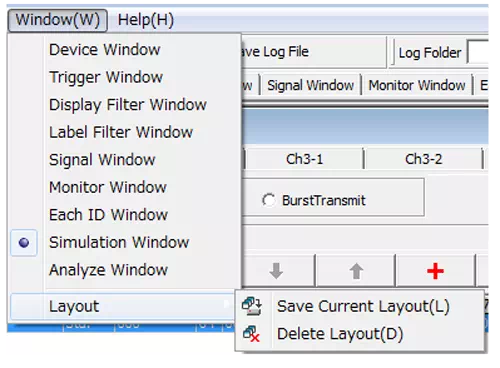
-
Assign a name and save
Enter any layout name in the dialog and click Save.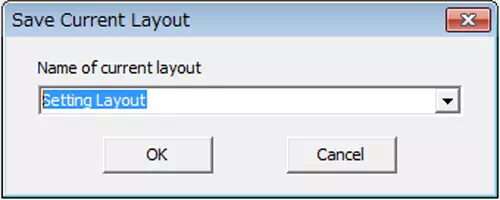
-
Recall a saved layout
Choose the target layout name from the dropdown. You can also click the button next to the selector to save the current layout.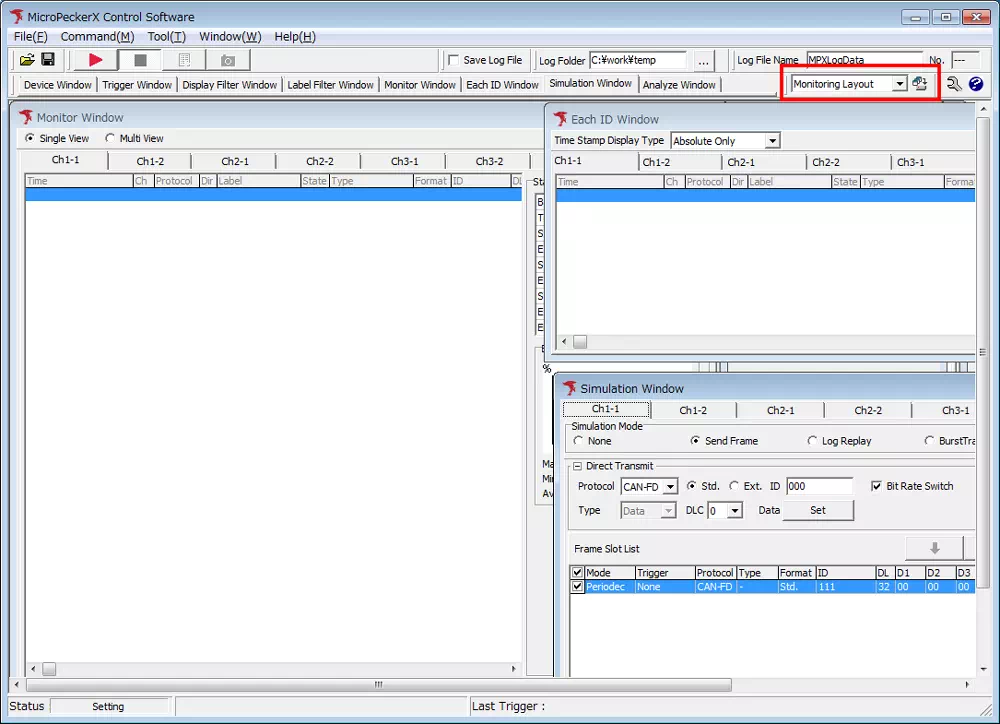
3. Configure Communication
Configure the MicroPeckerX CAN FD Analyzer for the target bus.
-
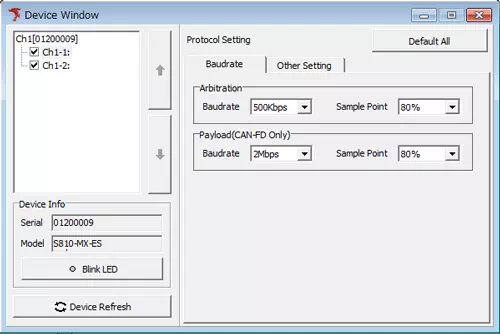
Open Device Window from the menu or toolbar.
-
Baud rate / Sample point
- CAN: Set the communication speed (for example, 500 kbps).
- CAN FD: Set the payload section baud rate and sample point.
-
ACK response
- Toggle the ACK response from MicroPeckerX between Enabled and Disabled.
-
Termination resistor
- Switch the bus termination resistor ON or OFF.
4. Arrange the Windows
Configure label display settings to make the communication results easier to understand. If you do not need this, proceed to the next section.
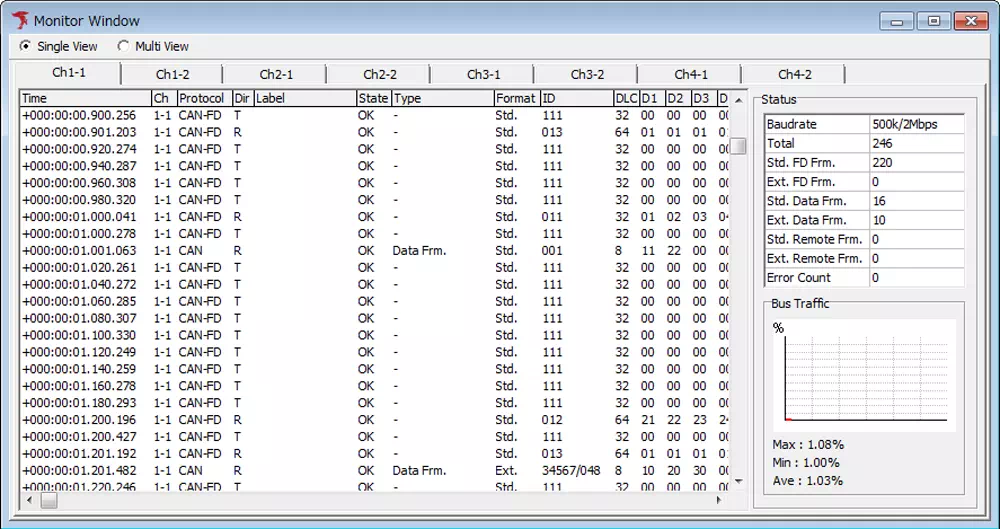
Label Filter Example
Setting label filters assigns label names and colors so the frames stand out.
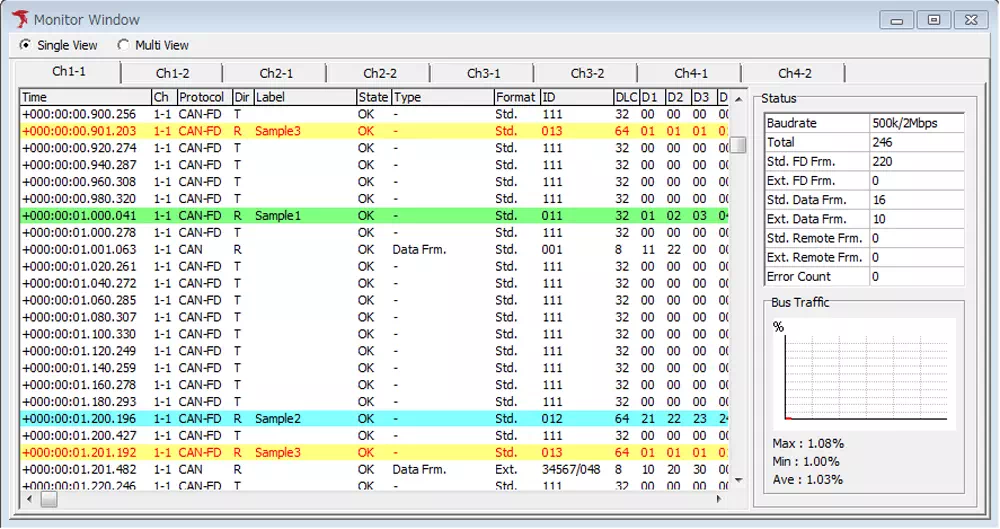
| Target ID | Label name | Background color |
|---|---|---|
| 011 | Sample1 | green |
| 012 | Sample2 | blue |
| 013 | Sample3 | yellow |
Before applying the label filter
After applying the label filter
Steps to Configure Label Filters
-
Open Label Filter Window from the menu or toolbar.
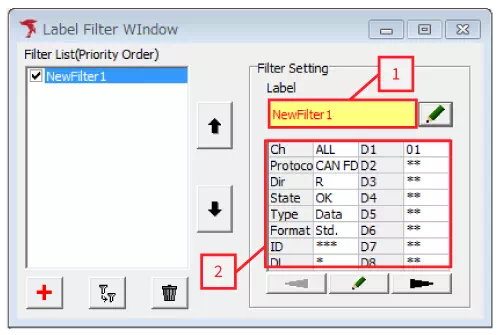
-
Add a filter
Click the + button to create a new label filter. -
Configure label appearance
- Double-click the label name column ([1]) in Filter Setting or click the pencil icon.
- Specify the font and background color in the dialog, then choose the appearance you prefer.
-
Configure the filter condition
- Double-click the condition column ([2]) in Filter Setting or click the pencil icon.
- Enter the criteria for the frames you want to label and click OK.
Once configured, color-coded labels appear in the log view so you can instantly identify specific frames.
5. Choose an Operating Mode
Choose how the MicroPeckerX CAN FD Analyzer operates. Decide whether you simply monitor the traffic or also transmit frames.
-
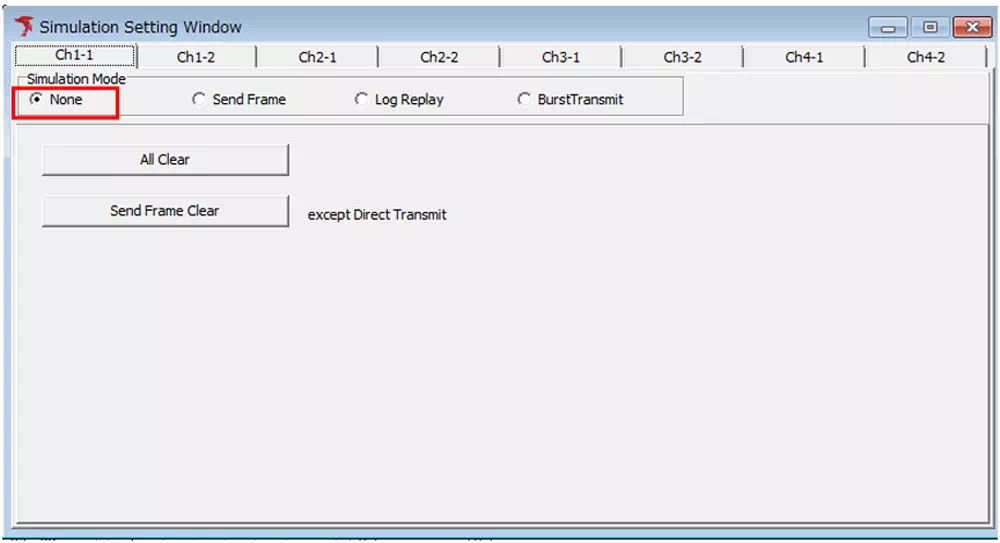
Open Simulation Window
Select Simulation Window from the menu or toolbar. -
Select a Simulation Mode
| Simulation Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| None | Monitors the CAN bus traffic without sending frames. |
| Send Frame | Allows you to configure periodic transmissions, send a single frame on demand, or define event-based transmissions that send multiple frames based on user actions. |
| Log Replay | Sends frames according to a pre-recorded transmission log. |
| BurstTransmit | Performs continuous transmission to apply a heavy load to the bus. |
For more details on each simulation mode, refer to xxxx.
6. Run the Analyzer
Click the ▶ button on the toolbar to start the MicroPeckerX operation. The window layout automatically switches to make it easier to monitor the communication log.
Layout before starting
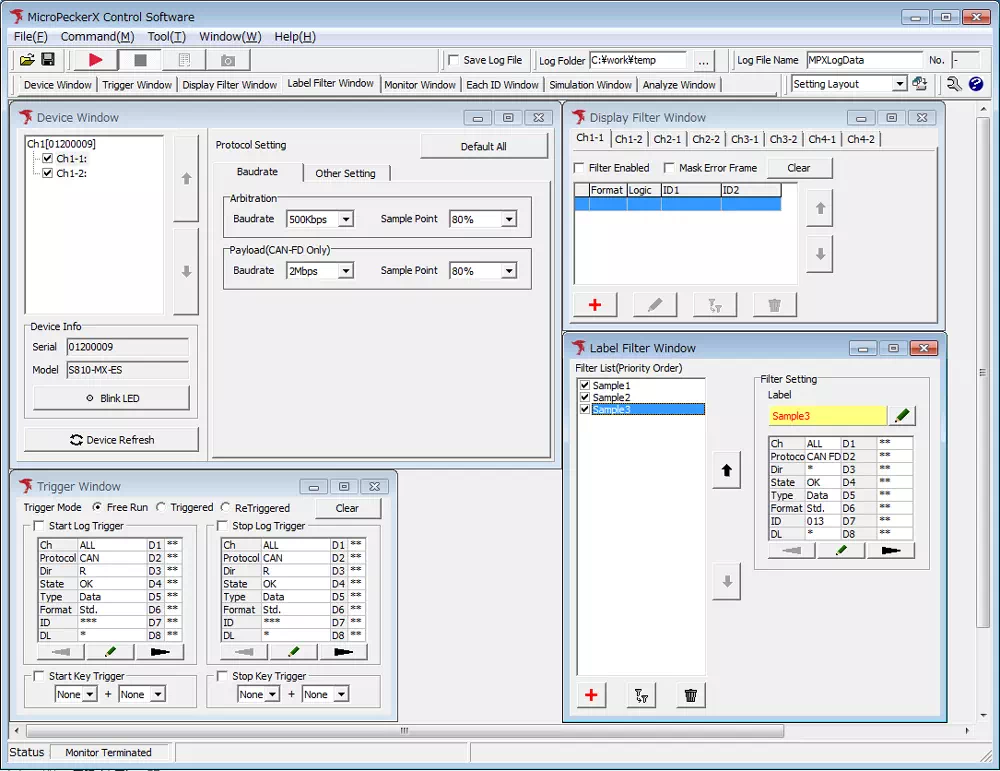
Layout while displaying communication logs
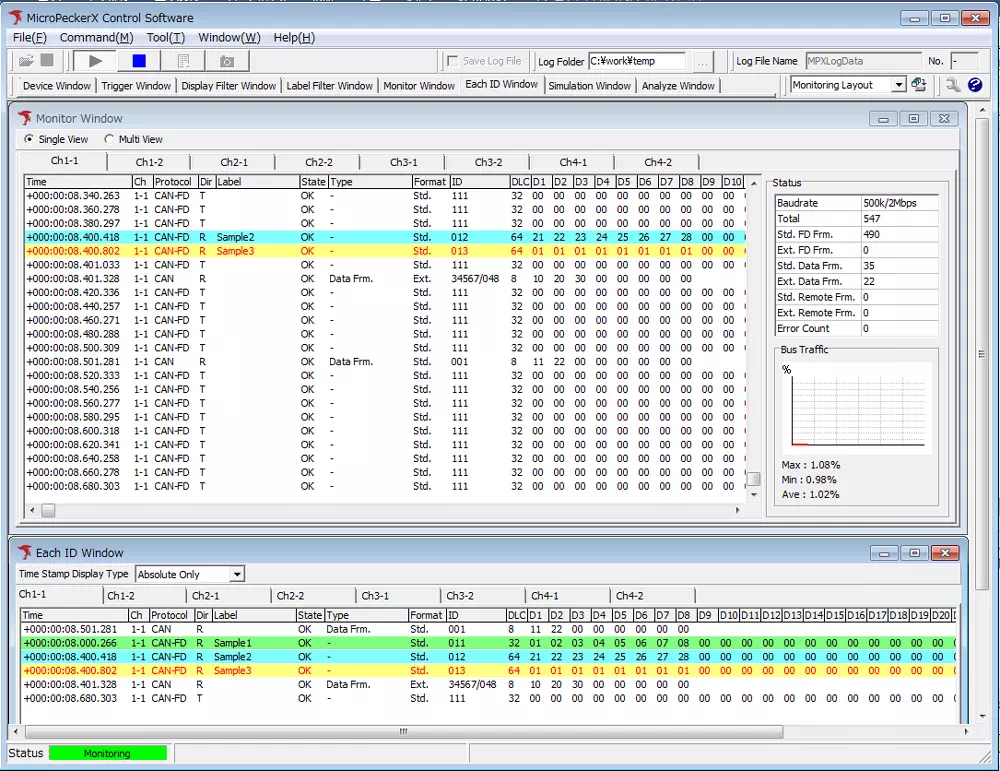
- Click ▶.
- The layout changes automatically and the communication logs appear.
7. Stop the Analyzer
Click the ■ button on the toolbar to stop communication. After stopping, the layout changes to the view best suited for reviewing logs.
Layout after stopping
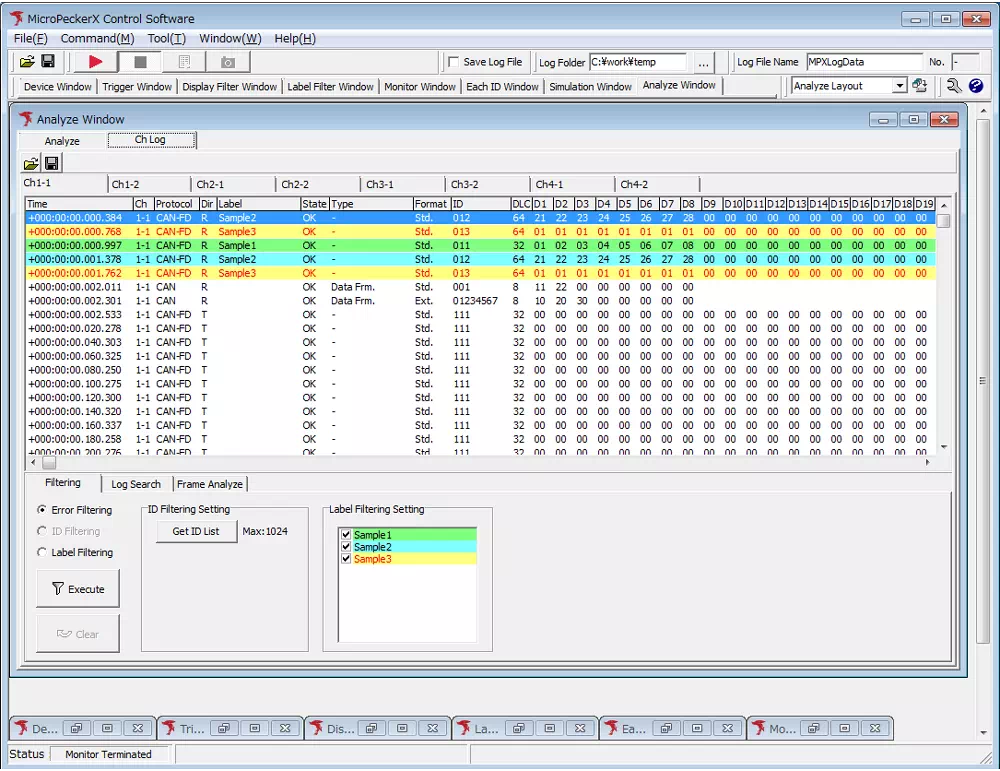
- Click ■.
- The layout automatically switches back to make it easy to review the logs.
8. Review and Analyze Logs
After stopping the operation, you can display and process the recorded logs. This section introduces the Search and Offset functions.
In addition to search and offset, MicroPeckerX CAN FD Analyzer provides the following analysis functions. Use them as needed.
- Frame Cycle Analyze
Visualizes and analyzes the transmission interval of CAN frames. - CAN Gateway Latency
Measures delay time and message loss when passing through a gateway. - CAN Gateway Residence
Checks the peak delay (residence time) when passing through a gateway.
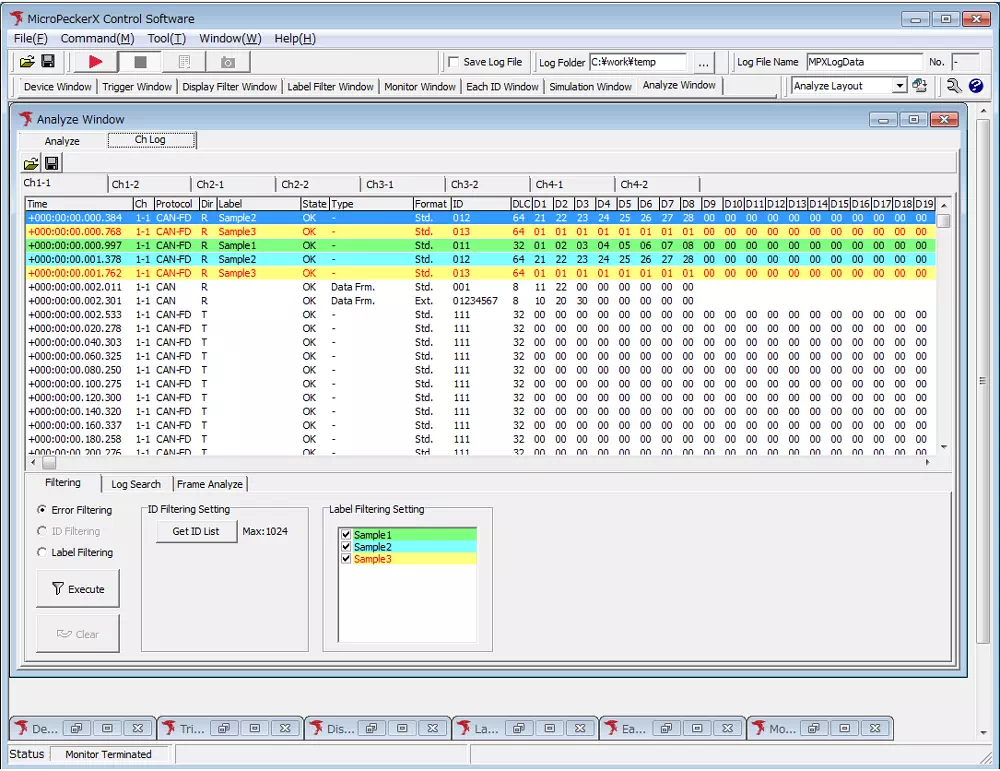
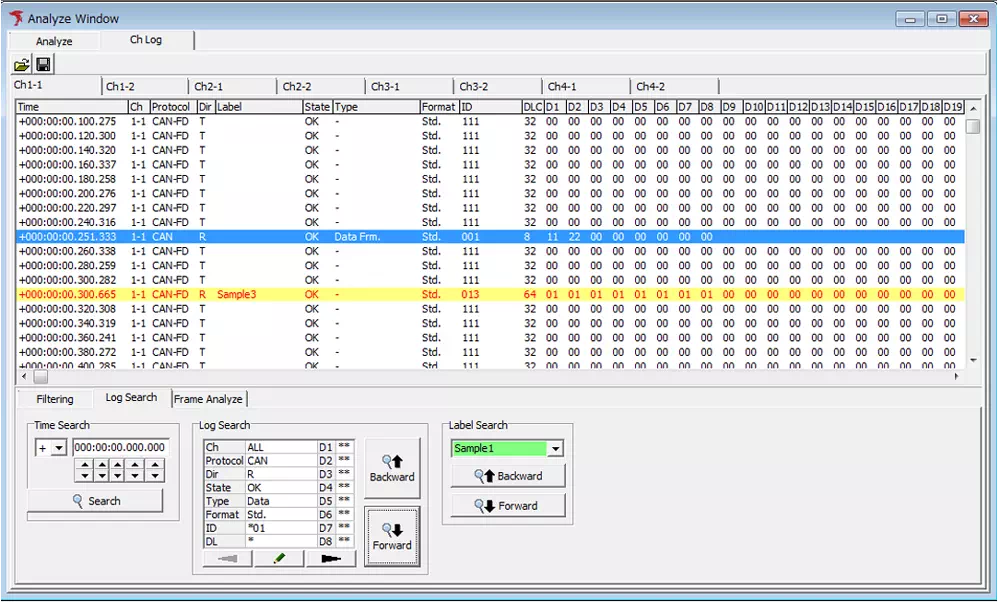
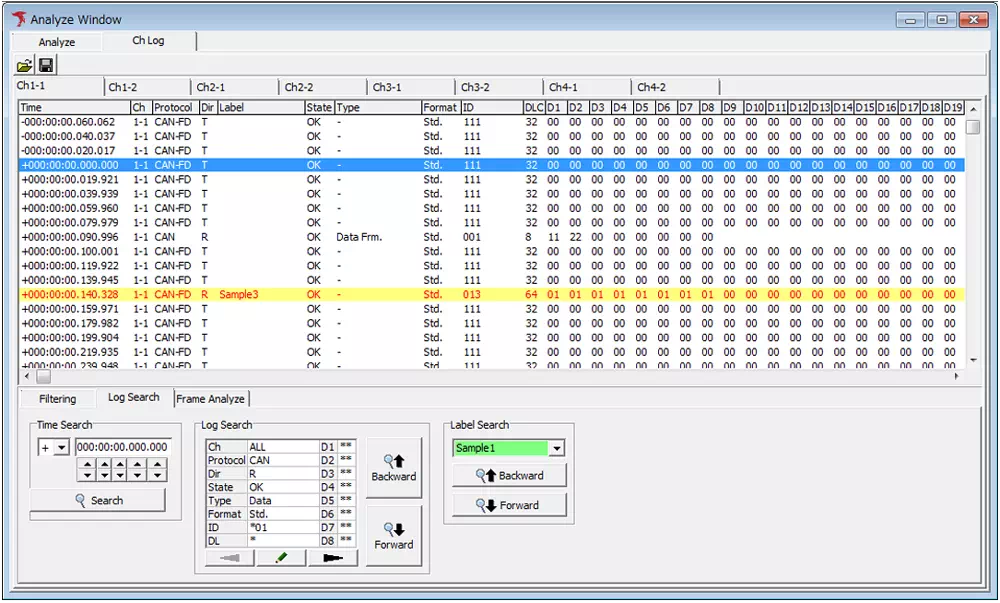
Search Function
To find a specific frame, specify the ID in the search box. Partial matches are supported; for example, searching for *01 highlights frames such as 0x001.
- Open the Log Search tab and click the pencil icon to display the Log Search dialog.
- Enter
*01in the ID field. - Click OK to close the Log Search dialog.
- Click the Backward or Forward button to select and highlight matching frames.
Log display before search
Log display after search
Offset Function
Use the offset function to check transmission intervals or relative time. You can designate any frame as the reference point and display the elapsed time from that frame for all other frames.
- Right-click the frame you want to use as the reference in the log view.
- Choose Set Offset from the context menu.
- The timestamp of the selected frame becomes zero.
- The other frames now display their relative time (offset) from the reference frame.
Display before setting the offset
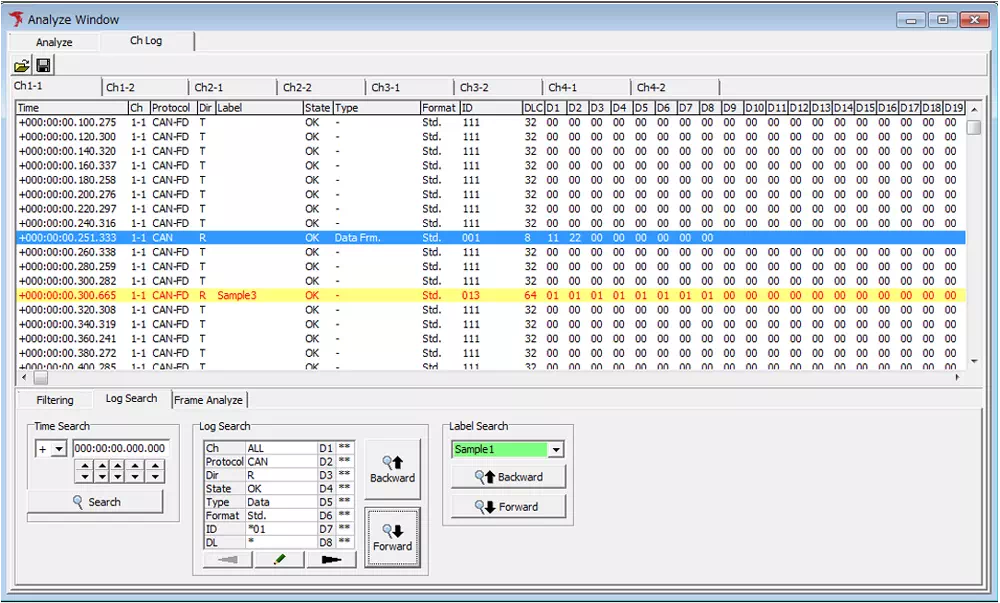
Display after setting the offset
With this feature, you can easily grasp the transmission intervals of other frames relative to the chosen reference frame.