Converting Between CAN and CAN FD
Use MicroPeckerX InstaGW to convert between CAN and CAN FD communication protocols.
Usage example
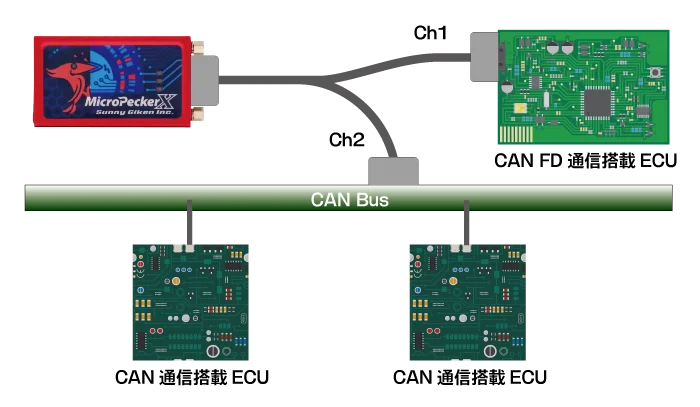
This example performs protocol gateway conversion between Ch1 (CAN FD) and Ch2 (CAN). The following sections show sample entries in the gateway setting file.
Common settings
Com sheet
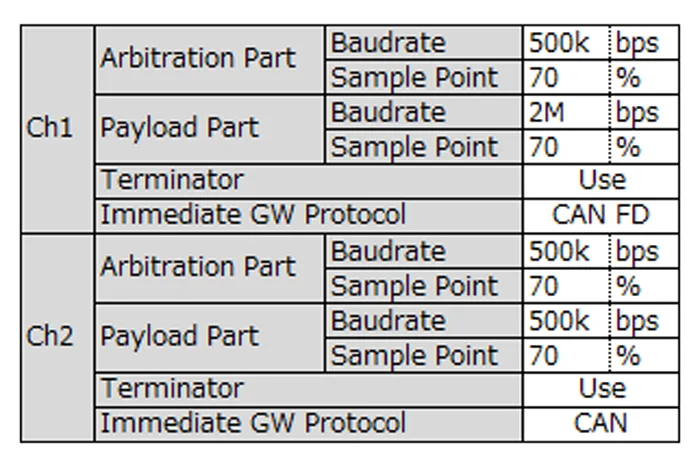
- Configure the arbitration and data-phase baud rates for each channel. In this example, Ch1 is configured for CAN FD and Ch2 for CAN.
- When using immediate gateway, the Immediate GW Protocol defines the protocol of each channel. In this example, Ch1 is CAN FD and Ch2 is CAN.
Using immediate gateway
Immediate GW sheet
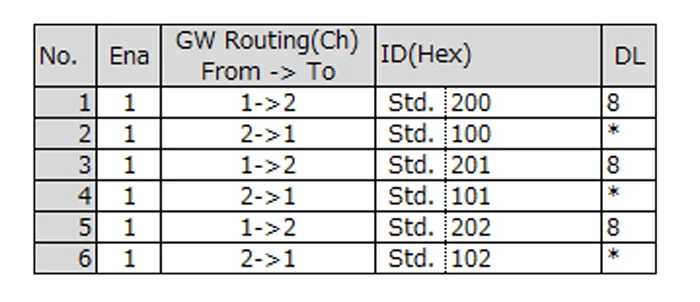
- Immediate gateway provides a gateway path with very little latency.*
- Configure the IDs to convert on each channel. In this example, IDs 200, 201, and 202 are forwarded from Ch1 to Ch2 (CAN FD → CAN), and IDs 100, 101, and 102 are forwarded from Ch2 to Ch1 (CAN → CAN FD).
- Up to 32 IDs can be configured for immediate gateway.
*Measured gateway latency of approximately 3.5 μs with CAN FD communication (arbitration phase 500 kbps, data phase 2 Mbps).
Using normal gateway
Gateway sheet
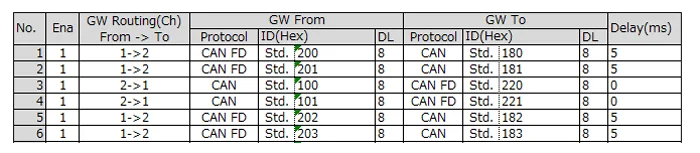
- Normal gateway* allows ID remapping and arbitrary transmission timing.
- Configure the IDs to gateway for each channel. In this example, the conversion 1→2 (Ch1→Ch2) changes the protocol from CAN FD to CAN. Gateway targets such as CAN ID 200 → CAN ID 180 demonstrate ID remapping.
- CAN IDs 200, 201, 202, and 203 received on Ch1 are forwarded to Ch2 with a 5 ms delay.
- Up to 64 IDs can be configured for normal gateway.
*Measured gateway latency of approximately 12.5–20 μs depending on data length with CAN FD communication (arbitration phase 500 kbps, data phase 2 Mbps).
Combining immediate and normal gateway
Immediate and normal gateway can be used together.
By combining up to 32 IDs of immediate gateway with up to 64 IDs of normal gateway, you can configure gateway processing for a maximum of 96 IDs.