Monitoring Screen Overview
This page explains the monitoring screens of the Message Authentication plug-in. Use them to check the transmission and reception status of security messages on the in-vehicle network and review the configuration for each ID in real time.
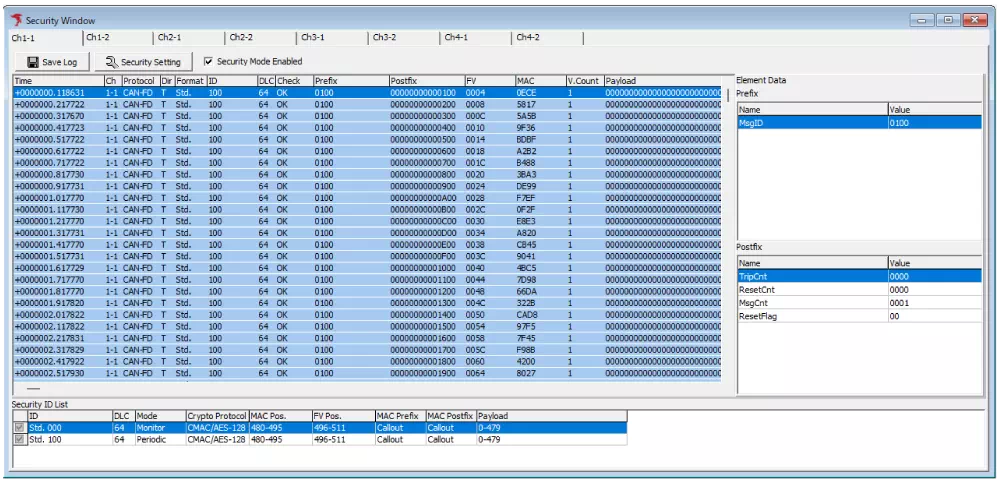
Security Message Log
The Security Message Log lists every security-related message that was sent or received. You can check details such as when the message was handled, which channel was used, what type of message it was, and whether authentication succeeded.
- When a communication issue or authentication failure occurs, you can immediately identify the ID, timestamp, and cause.
- During security validation or log analysis, you can trace the state changes of each message chronologically.
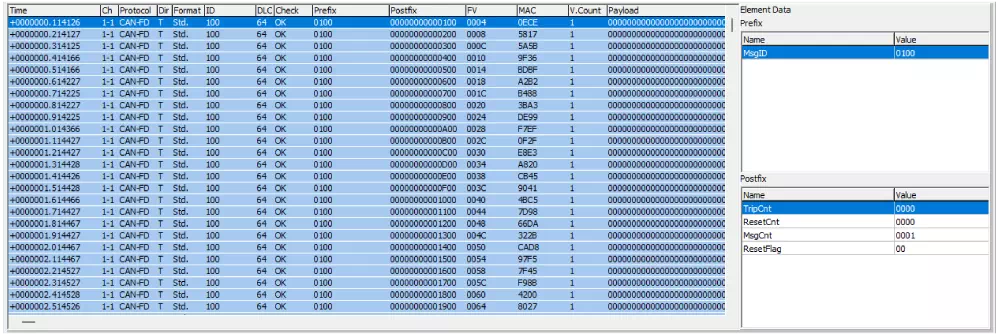
| Main Section | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Log display area | Shows the security messages that were sent or received. | |
| Time | Displays the send/receive time. Uses the format configured in “Time Stamp Form” in the Option dialog. | |
| Ch | Displays the channel that sent or received the message. | |
| Protocol | Shows the protocol type (CAN/CAN FD). | |
| Dir | Shows the direction of communication. “T” indicates transmit and “R” indicates receive. | |
| Format | Displays the CAN ID type. “Std.” stands for standard ID and “Ext.” stands for extended ID. | |
| ID | Displays the CAN ID. | |
| DLC | Shows the data length. | |
| Check | Displays the MAC verification result (OK/NG). OK means authentication succeeded, NG indicates an authentication error. | |
| Prefix | Shows the prefix value in hexadecimal. (*1) | |
| Postfix | Shows the postfix value in hexadecimal. (*1) | |
| FV | Displays the FV (Freshness Value). (*1) | |
| MAC | Displays the authentication MAC value. (*1) | |
| V.Count | Shows the number of MAC verifications. | |
| Payload | Shows the data field (payload) values. (*1) | |
| Element Data (*2) | Prefix | Displays the prefix elements of the security message selected in the log area. (*3) |
| Postfix | Displays the postfix elements of the security message selected in the log area. (*3) | |
*1: Each item is displayed left-aligned in big-endian format. *2: Hidden while monitoring is active. *3: Element Data uses the display format shown below. The available fields depend on the Element Setting configuration.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Shows the element name. |
| Value | Displays the element value (hexadecimal) right-aligned in big-endian format. |
Security ID List
The Security ID List screen shows the authentication parameters for every configured CAN ID. You can immediately review how each ID is configured.
- When multiple IDs have different authentication settings or you suspect a configuration mistake, you can review everything at once.
- Easily check which IDs have authentication enabled and whether they follow your operational rules.

| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | Displays the configured CAN ID. “Std.” indicates a standard ID and “Ext.” indicates an extended ID. |
| DLC | Shows the data length. |
| Mode (*1) | Shows the transmission mode for the message. ・Monitor: Receive-only messages ・Periodic: Periodic transmit messages (data frames are sent at the interval specified in Cycle under Target Frame Info) |
| Crypto Protocol | Displays the cryptographic protocol used to generate the MAC. |
| MAC Pos. | Shows the bit position in the data field where part of the MAC is placed, using the “Motorola sequential” notation. For example, “40-63” means that bits 40–63 (bytes D6 to D8) in the data field contain the upper 24 bits of the MAC. |
| FV Pos. (*2) | Shows the bit position in the data field where the FV is placed, using the “Motorola sequential” notation. For example, “32-39” means that bits 32–39 (byte D5) in the data field contain the FV. |
| MAC Prefix | Displays the source used to generate the MAC prefix. (*3) |
| MAC Postfix | Displays the source used to generate the MAC postfix. (*3) |
| Payload | Shows the bit positions in the data field treated as payload data for MAC generation, using the “Motorola sequential” notation. For example, “0-31” means that bits 0–31 (bytes D1 to D4) in the data field are treated as payload. |
*1: “Monitor” is receive-only. “Periodic” transmits at regular intervals. *2: Displays “NotUsed” when FV is disabled. *3: Displays “Callout” when using values generated by a callout DLL, or “NotUsed” when not used.